Hello, friends today we are discussing Analysis of
Trusses. It’s an important topic in Structural Analysis and those who want to
Structural Designer about it in the future.
This article we are covering the basic structural portion. So friend read the article completely, and
quarry about this article please comment below.
So, Let’s Start –
What is Truss?
In one sentence, a truss is a composed of slender bars joined together at their endpoints.
In our surroundings, we are daily seen various types of trusses. Truss design is very important for bridge design because of the maximum bridge in our surrounding made by trusses, mainly railway bridges.
Trusses are composed bar, the end connection are usually formed by bolting or welding the ends of the bars to a common plate, called gusset plate or by simply passing a large bolt or pin through each of the members.
What is Plane Truss?
If all members, as well as forces acting on it, lie in a the simple plane then the truss is called plane truss.
What are the assumptions made for the design of a truss?
We all know that when we design some structural elements, we have to take something for our own benefit. So here it is first necessary to determine the force i.e. the internal force, developed in each member when the truss is subjected to given loading.
In regard, the following assumptions are made:
The forces are applied at the joints, any loads that act between joints are split into equivalent support ends reactions and added to the joint loads.
The member are joined together by all truss's element joints
are considered as pin connection since there is always axial force only and for
the sake of analysis and design forces.
The members cannot develop moments in the end.
The members are subjected to purely axial forces.
Each member is acted upon by two force system and therefore
the forces at the ends of the member must direct along the axis of the member.
Self-weight of the truss can be ignored or at least assumed
to be equally distributed as loads at the joints.
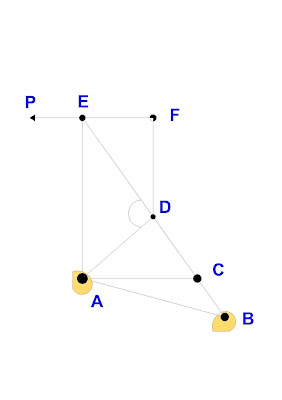
What is zero force members?
Zero force members are the members who do not carry any load, i.e. the member is not under tension or in compassion. These zero force members are used to increase the stability of the truss during construction and to provide support if the applied load is changed. The zero-force members of truss can generally be determined by inspection of each of its joints.
 |
| zero-force member |
How to determined/identify zero force members?
There is two ways to determining zero force members theoretically or mathematically. But we engineers have some general rules for determining zero force members easily.
At a two-member joint: If those members are not parallel and there are no other external loads (or reactions) at the joint then both of those members are zero force members.
In a three-member joint: two members are collinear, the third member is always a zero force member provided that no external force or support reaction is applied to the joint.
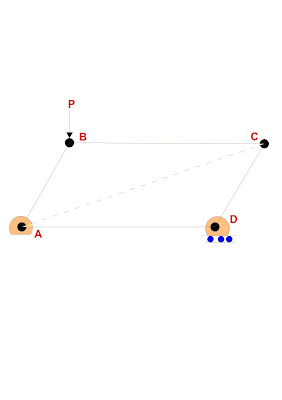
What is a simple truss?
To prevent collapse, the truss must be rigid. To illustrate this consider the truss in below fid. Here four-bar namely AB, BC, CD, and DA form a truss. Now if a load P is applied to it at D, the truss will collapse. Therefore, it is required to add one bar AC to make the structure rigid. The simplest form that is rigid and stable is a triangle.
For a statically determine truss the following relationship must be satisfied.
M = 2j – 3, where m is the number of members and j is the number of joints
If m> 2j – 3, the structure will be statically indeterminate and if m< 2j – 3 the structure will not be rigid.
 |
| simple truss |






3 Comments
good
ReplyDeleteOk, nice
ReplyDeleteNice elaborate
ReplyDelete